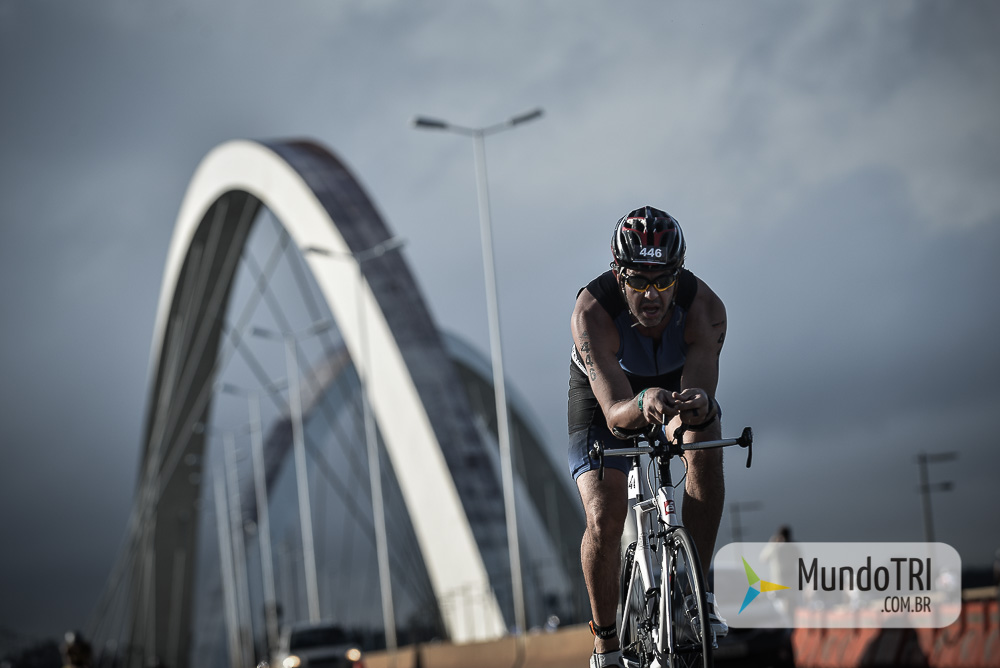
Last weekend, I had the good fortune and honor to host professional triathlete Tim Don at my home during his four-day visit to Brasilia to compete in Sunday’s 70.3 Ironman triathlon (Race Highlights). Since I was also training for the race, I was particularly enthusiastic about spending time with a triathlete who won four world titles, represented the United Kingdom at three Olympic games, and is currently ranked as one of the top triathletes in the world.
Tim won Sunday’s Brasilia 70.3 Ironman race setting a course record by completing the 1.8 km swim, 90 km bike, and 21 km run course in 3 hours and 46 minutes. Yes, that is very fast! Given that I finished my race 751 positions behind Tim, I thought I would ask him to share the keys to his success. Tim highlighted three essential factors associated with training and racing: consistency, communication, and performance. What was curiously absent from Tim’s response was the focus on results, but more on that later.
Based on Tim’s successes and the fact that he has never been sidelined due to overtraining, illness, or injury, I wanted to discover what I could incorporate in not only my own training but also my professional and personal lives. This is what I learned.
Communication
The maxim, “where there’s smoke, there’s usually fire” is not only apropos to sport but to all facets of our lives. Tim’s approach is to address problems immediately and directly as soon as they are identified, rather than waiting until the same problem has surfaced on multiple occasions. Regular communication with his support team ensures that any potential injuries are identified and corresponding preventive actions are taken.
While everyone understands the importance of addressing problems as soon as they are encountered, the transference of this philosophy to practice can prove to be more challenging. The goal to ensure our students are receiving the best education possible is achieved through open, honest, and timely communication, which is dependent on the partnership between parents, students, and the school. This partnership is similar to a three-legged stool; if one of the legs is missing, the stool cannot stand on its own. If an educational program is not standing on its own, then it will be difficult to overcome inevitable conflicts and challenges. A passive aggressive or “head in the sand” approach to a problem will not resolve the issue. It is only through open, honest, and expedient communication that we will effectively work together to support our students.
 Consistency
Consistency
Tim stressed that consistency does not refer to always performing at the highest level each week, but, rather, being faithful to a carefully established plan that is designed to move us forward, in an incremental manner, toward our goal. His words reminded me of a prior blog post about the 20-Mile March and the importance of not wavering from a consistent and iterative approach.
When preparing for a marathon, we are not going to start training by running 30 kilometers on the first day. Rather, we will start with a short distance and gradually build up our endurance over time through a consistent adherence to an established plan. The concept is the same for students. Deeper levels of learning are achieved through a regular dedication to study and class attendance, rather than trying to cram for tests during short, intense periods. The former approach will normally result in lasting development and understanding while the outcome of the later is, at best, a fleeting recall of the information associated with the test questions.
Performance
I was initially surprised that Tim focused on performance rather than results, especially given that his livelihood depends on winning. However, after reflecting on his words, his approach resonated with me. By way of example, there is a significant difference between finishing a race in third place, ten seconds behind the winner, and finishing in third place, ten minutes behind the winner. While a third place finish is a good result, it may not necessarily equate to a good performance. A focus only on results, with the accompanying pressure and stress, may often lead to burnout, injury, and diminished performance. In contrast, your best performances will usually lead to great results. In terms of his professional competitions, Tim states the following:
“Some of my best performances have come from races where I have not been on the podium but I have squeezed our every bit of what I had and, as they say, left nothing out there. I truly walked away with a smile knowing that, sure the win would have been nice, but, on that day, that’s what I had. Control what you can control. I really try to race like that in every race. I will sprint as hard for 40th position as I would for the win: that’s me, that’s what I do, that’s what I was taught to do.”
Reflecting on these words in the context of our student athletes who are currently competing at the Big 4 tournament, performance is the key. While we hope students at the American School of Brasilia (EAB) achieve outstanding results, it is their performance, both individually and collectively, that is of great importance. Win or lose, we will have much to celebrate if our students are able to perform at their highest levels and “leave nothing out there.”
Transferring this concept to academics, EAB does not narrow the definition of teaching and learning to one where teachers only prepare students for tests (results). Instead, education at EAB is about students developing in a holistic manner where the school supports the whole child to achieve his or her potential (performance). Through effective communication, a consistent approach to learning, and a focus on performance, outstanding results will naturally follow, as exemplified through the impressive successes and achievements of EAB students.
Congratulations to Tim Don for his performance at the Brasilia 70.3 ironman race (Interview / 48 Hours with Tim Don)
Photo Credits: Wagner Araújo and Mundotri (http://www.mundotri.com.br/)
Desempenho
No final de semana passado, eu tive a sorte e a honra de hospedar o triatleta profissional Tim Don na minha casa, por quatro dias, durante sua visita à Brasília para competir no Ironman 70.3, no domingo (Race Highlights). Como eu também estava treinando para a corrida, eu estava particularmente entusiasmado em passar algum tempo com um triatleta que ganhou quatro títulos mundiais, representou o Reino Unido em três Jogos Olímpicos, e atualmente, está classificado como um dos melhores triatletas do mundo.
Tim ganhou a corrida do Ironman 70.3 de Brasília no domingo, estabelecendo um recorde ao completar os 1.8 km de natação, os 90 km de bicicleta e os 21 km de corrida, em 3 horas e 46 minutos. Sim, isso é muito rápido! Tendo em vista que eu terminei a minha corrida 751 posições atrás do Tim, eu resolvi pedir a ele para compartilhar a chave do seu sucesso. Tim destacou três pontos-chave associados ao treinamento e às corridas: consistência, comunicação e desempenho. O que curiosamente ficou ausente da resposta de Tim foi o foco em resultados. Mas falaremos sobre isso mais tarde.
Baseado no sucesso do Tim e no fato de que ele nunca foi afetado devido ao excesso de treinamento, doença ou lesão, eu queria descobrir o que eu poderia incorporar, não só na minha própria formação, mas também na minha vida profissional e pessoal. Isto foi o que eu aprendi.
Comunicação
A máxima, “onde há fumaça há, geralmente, fogo” . Isso não é apenas referente ao esporte, mas à todas as facetas de nossas vidas. A abordagem do Tim é de resolver os problemas de imediato e de forma direta, logo que são identificados, em vez de esperar até que o mesmo problema venha à tona em diversas ocasiões. A comunicação regular com sua equipe de apoio garante que quaisquer possíveis lesões sejam identificadas, e que ações preventivas correspondentes possam ser tomadas.
Enquanto todo mundo entende a importância de abordar os problemas assim que eles são encontrados, a transferência desta filosofia para a prática pode revelar-se mais desafiadora do que imaginamos. O nosso objetivo para garantir que nossos alunos estejam recebendo a melhor educação possível é alcançado através de uma comunicação aberta, honesta e oportuna, que é dependente da parceria entre pais, alunos e escola. Esta parceria é semelhante à um banquinho de três pernas; Se uma das pernas estiver faltando, o banco cairá. Se um programa educacional não estiver de pé por conta própria, então será muito difícil que ele consiga superar os conflitos e desafios, que são inevitáveis. Uma abordagem passiva-agressiva não vai resolver um problema. Somente através de uma comunicação aberta, honesta e conveniente é que vamos trabalhar de forma eficaz e em conjunto para apoiar os nossos alunos.
 Consistência
Consistência
Tim salientou que, a consistência não se refere à realização de níveis mais altos a cada semana, mas sim, ser fiel a um plano estabelecido cuidadosamente, que é projetado para mover-nos para a frente, de forma incremental, em direção ao nosso objetivo. Suas palavras me fizeram lembrar de um post anterior sobre a Marcha das 20 Milhas e a importância de não vacilar a partir de uma abordagem consistente e interativa.
Ao nos prepararmos para uma maratona, não vamos começar a treinar correndo 30 quilômetros no primeiro dia. Em vez disso, vamos começar com uma curta distância e gradualmente construir a nossa resistência ao longo do tempo, através de uma adesão consistente com um plano estabelecido. O conceito é o mesmo para os alunos. Níveis mais profundos de aprendizagem são alcançados através de uma dedicação regular de estudo e frequência nas aulas, e não com testes intensos em curto prazo. A primeira abordagem, normalmente, resulta no desenvolvimento e entendimento duradouro, enquanto que o resultado do último é, na melhor das hipóteses, uma recordação fugaz da informação associada às perguntas do teste.
Desempenho
No início eu fiquei surpreso ao saber que o Tim focava no desempenho ao invés dos resultados, especialmente tendo em conta que a sua sobrevivência depende da vitória. No entanto, após refletir sobre suas palavras, sua abordagem ressoou em mim. Por exemplo, há uma diferença significativa entre terminar uma corrida em terceiro lugar, dez segundos após o vencedor, e terminar em terceiro lugar, dez minutos atrás do vencedor. Enquanto terminar em terceiro lugar pode ser um bom resultado, pode não ser necessariamente, um bom desempenho. Os resultados como foco, com pressão e estresse, podem muitas vezes levar à exaustão, ferimentos e desempenho reduzido. Em contraste, as suas melhores performances normalmente irão levar à grandes resultados. Em relação as suas competições profissionais, Tim afirma o seguinte:
“Alguns dos meus melhores desempenhos vieram de corridas onde eu não estive no pódio, mas as que eu dei tudo o que eu tinha, e como costumam dizer, não deixei nada para trás. Eu realmente saio com um sorriso, sabendo que, com certeza, a vitória teria sido boa, mas, naquele dia, é o que eu tinha pra dar. Controle o que você pode controlar. Eu realmente tento correr assim em todas as corridas. Eu vou dar o meu melhor sprint para a 40º posição, assim como eu daria para a vitória: Esse sou eu, isso é o que eu faço, é o que eu aprendi a fazer.”
Ao refletir sobre essas palavras no contexto dos nossos alunos atletas que estão atualmente competindo no torneio Big 4, o desempenho é a chave. Enquanto esperamos os alunos da EAB alcançarem excelentes resultados, é o seu desempenho, tanto individual como coletivo, que é de grande importância. Ganhando ou perdendo, nós teremos muito a comemorar, se nossos alunos forem capazes de desempenhar suas habilidades em alto nível e “não deixarem nada de fora”.
Transferindo este conceito para o lado acadêmico, a EAB não define o ensino e a aprendizagem como apenas um preparo para testes (resultados). Em vez disso, a educação na EAB faz com que os alunos se desenvolvam de uma forma holística, onde a escola possa apoiar a criança como um todo, alcançar o seu potencial (desempenho). Através de uma comunicação eficaz, uma abordagem consistente à aprendizagem, e um foco no desempenho, resultados excelentes virão naturalmente, exemplificados através do sucesso e das realizações dos alunos da EAB.
Photo Credits: Wagner Araújo and Mundotri (http://www.mundotri.com.br/)
Addendum
Since several people asked about the race course, I have included the course maps below (click to enlarge).
Swim Course:
Bike Course (3 loops)

Run Course (3 loops)





















